TUMGAD
Exercise generation and helpful materials for the Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures 📚
Prim’s Algorithm
Jarnik Prim’s algorithm takes a weighted, normally undirected graph and produces the minimal spanning tree of that graph.
A minimal spanning tree of a graph contains the same nodes as the original graph, but only a subset of the edges, those edges that keep the nodes connected, but have a minimal weight.
For this the algorithm starts at a given node and then adds the neighboring node with the smallest edge-weight to the graph:
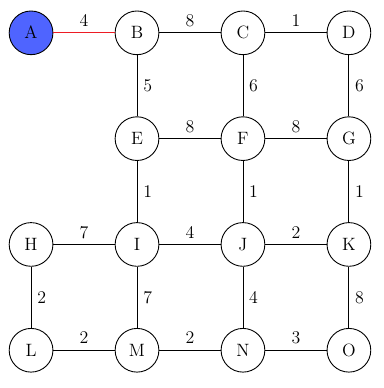
Now the graph already consists of two nodes (A and B) and the process begins anew. The next node to be added is E, as the edge weight 5 is the lowest possibility.
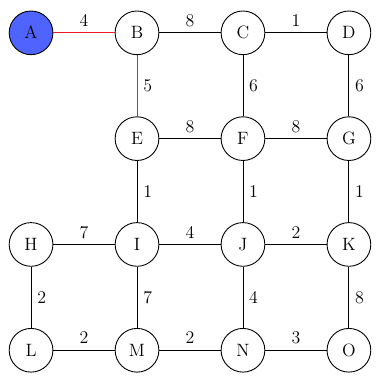
Now there are 3 possible connections (C, F, I) since the edge to node I has the smallest cost, we add it to the graph…
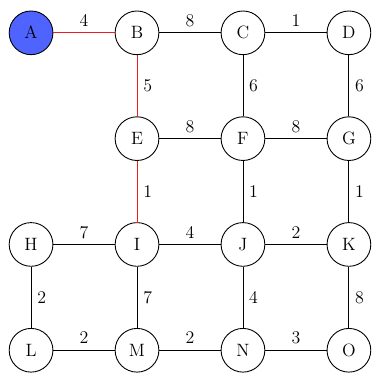
This simple process continues until we have added all the nodes to our graph:
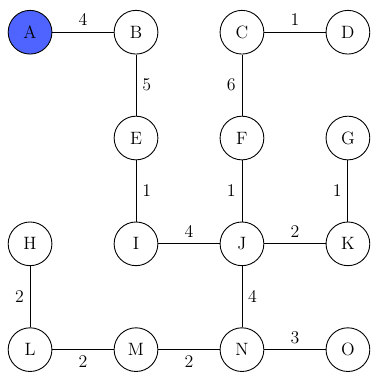
In the case of equal edge weights the algorithm proceeds lexicographically.